Five companies that are revolutionising humanoid robotics
In just a few years, humanoid-looking robots have gone from starring in science fiction films to becoming a tangible reality. Companies such as Boston Dynamics, Tesla and Agility Robotics are spearheading a transformation of what is presumed to be the great industrial revolution of the 21st century, in which humans and robots will share the same workspace, interacting in a natural way.
Today, humanoid robots are not only able to walk, climb stairs, or move boxes in a warehouse, but they do so with agility and precision, thanks to sophisticated sensors and intelligent algorithms. Moreover, the integration of generative AI with mechatronic systems is endowing these machines with cognitive and physical abilities that previously seemed impossible, such as seeing, "reasoning" or making increasingly autonomous decisions.
In this new scenario, companies around the world are competing to lead the way in the development of robots capable of taking on tasks in industry, services or even the home. Here we explore five companies that are leading the way.
Boston Dynamics
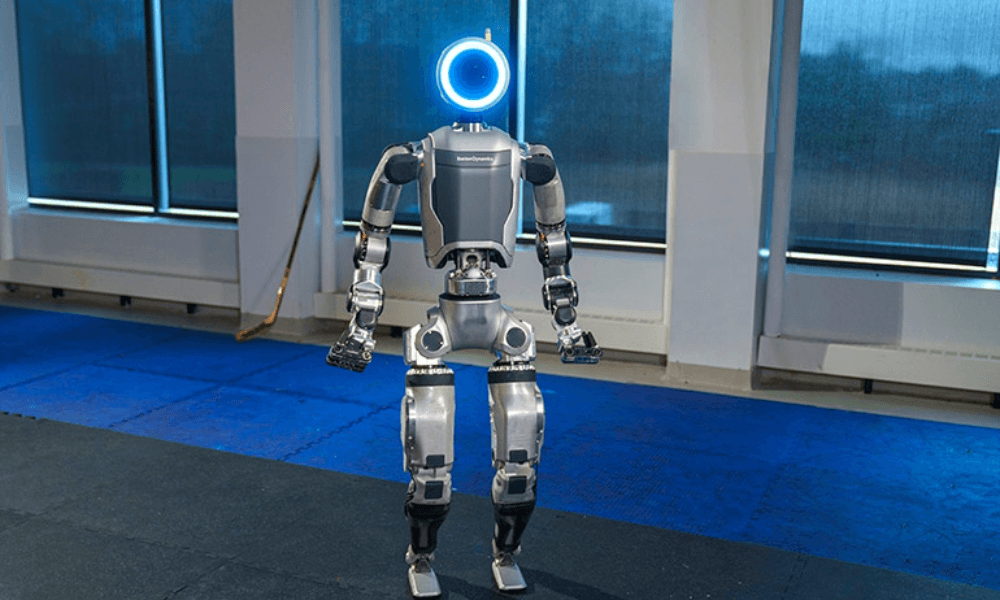
Boston Dynamics is considered one of the most advanced companies in the field of industrial robotics and its developments have redefined what we understand by robotic dexterity, with machines capable of executing complex movements that until recently seemed exclusive to the human body.
Their focus is on providing robots with exceptional agility and coordination, combining advanced actuators, real-time control algorithms and highly innovative mechanical designs. Over the past few years, the company has repeatedly demonstrated that many of its robots can balance on uneven surfaces, walk on inclines, jump with precision, perform somersaults and even perform parkour routines with impressive stability.
Boston Dynamics' most interesting robot is Atlas, a bipedal humanoid approximately 1.5 metres tall, initially developed as a research platform. Its latest version incorporates electric actuators that give it greater power and precision, with the goal of surpassing human performance in strength and flexibility. While Atlas is still a prototype (it is not freely marketed), its development points the way to a new generation of industrial robots.
Alongside Atlas, Boston Dynamics has also developed other robots that, although they do not follow a human form, have been key to positioning itself among the leading companies in the sector. These include Spot, an autonomous quadruped used in industrial inspections, rescue and surveillance; and Stretch, a mobile platform with robotic arms designed to automate logistics tasks in warehouses.
Tesla (Optimus)
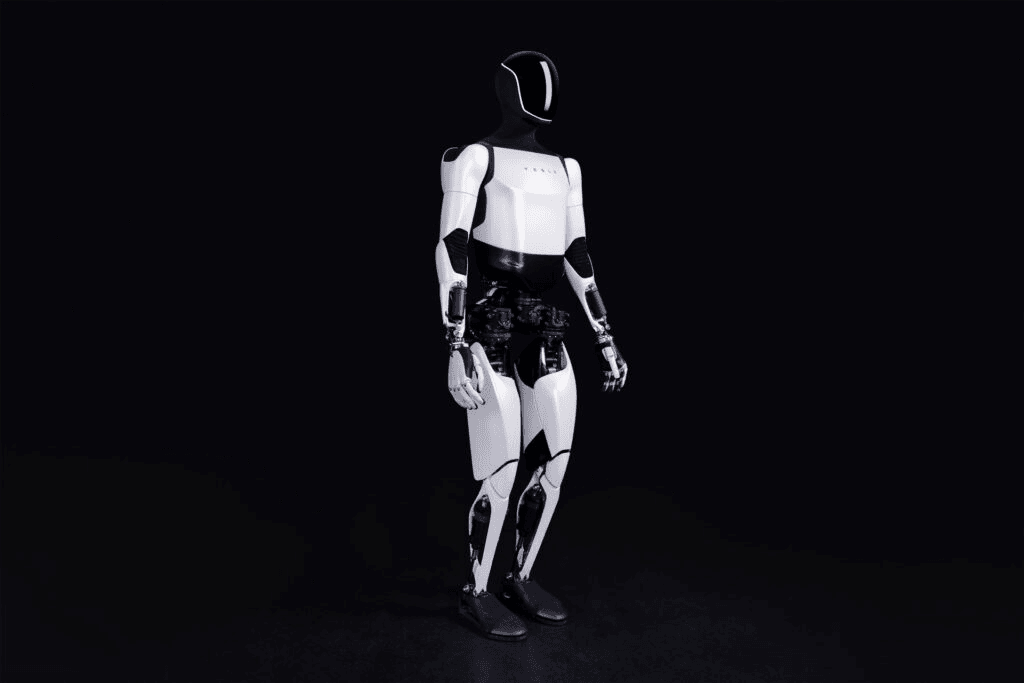
Tesla, the company best known for its electric vehicles and advances in autonomous driving, broke into the world of humanoid robotics in 2021 by announcing its Optimus robot, a humanoid robot approximately 1.73 metres tall and weighing 56 kg.
Tesla's major differentiator in humanoid robotics lies in its vertical integration of technologies and a clear focus on the consumer market. Coming from the automotive sector, the company inherits all the expertise it has developed for its autonomous vehicles in areas such as electrical systems, actuators, batteries and especially artificial intelligence applied to environmental perception.
This allows it to develop its robot as an integral platform, in which all the components are designed and manufactured by the company itself, instead of assembling parts from third parties, which in turn lays the foundations for future scale production.
Another key to the project lies in its artificial brain. Its integration with Grok, the LLM developed by xAI (Elon Musk's artificial intelligence company) allows it not only to execute direct commands, but also to understand natural language, interpret complex commands and learn new tasks.
As he has stated on multiple occasions, Elon Musk envisions a not-too-distant future in which millions of humanoid robots perform dangerous, repetitive or tedious jobs, so Optimus could become a "universal worker" capable of handling tasks ranging from assembling parts in a factory to helping with household chores.
Agility Robotics
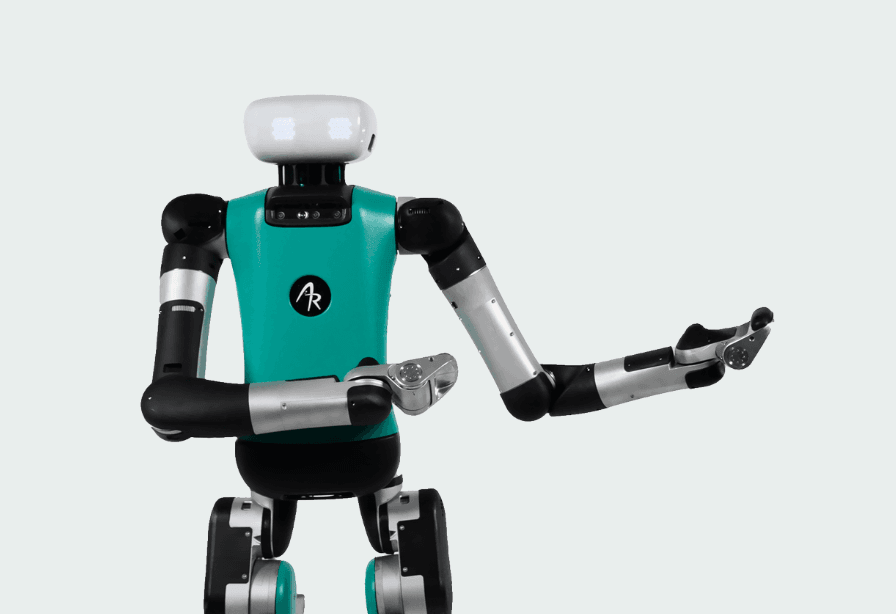
Agility Robotics is a pioneer in the development of humanoid robots. Unlike other companies that are still in the research and development phase of advanced prototypes, Agility is committed to practical solutions, especially in sectors such as logistics and industry.
In this sense, Digit, its most outstanding robot, has been one of the first to operate in real warehouses, collaborating with human workers in tasks as heavy as moving and lifting boxes. At a height of 1.75 metres, Digit has demonstrated that it can move easily through narrow aisles or uneven surfaces, making it ideal for facilities not suited to traditional automation. This saves companies from having to rethink their spaces to accommodate robots.
Large companies such as Amazon have already started to test them in their warehouses and, in the case of the e-commerce giant, they are also studying the possibility of them becoming the future deliverers of all types of orders. In terms of technology, Digit combines advanced sensors (LIDAR, stereo cameras, force sensors) with control algorithms and machine learning that allow it to balance itself, plan routes and adapt to new tasks.
In addition, Agility collaborates with companies such as Nvidia to improve its perception and learning capabilities through simulations and AI modelling. Its stated goal is to be able to manufacture up to 10,000 units per year, making it a common "tool" in all types of factories and distribution centres.
Hanson Robotics
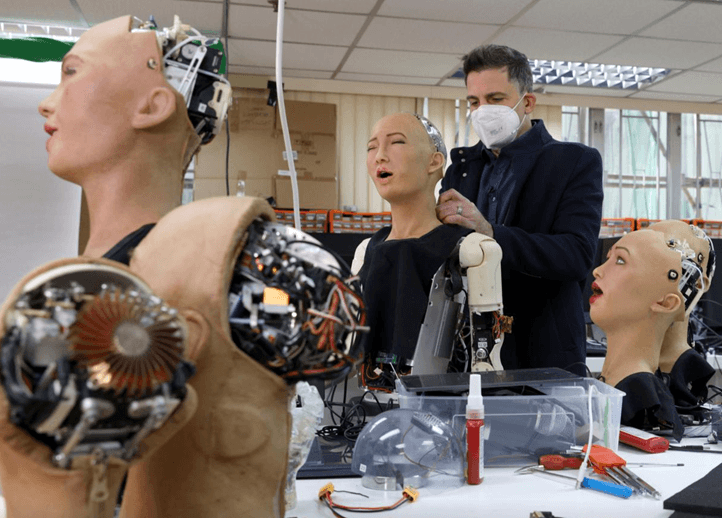
Hanson Robotics is a company specialising in the development of humanoid robots with social intelligence, focusing on emotional interaction and communication with people .
This translates into a series of androids with realistic human features that have the ability to hold fluid conversations, thus positioning themselves in areas such as education, customer service, marketing or social accompaniment.
Its best-known robot is Sophia, introduced in 2016, which became world famous for its facial expressiveness and ability to hold natural dialogues. Sophia was designed to simulate emotions, using a special material called Frubber that allows her to express complex gestures such as a smile or a frown. Complex servomotor and sensor systems operate under her 'skin', while on the cognitive side she uses artificial intelligence to interpret language, recognise faces, remember conversations and generate responses.
In addition to Sophia, Hanson has developed versions aimed at specific audiences: Grace is designed to care for the elderly; Little Sophia is intended to teach programming to children; and other androids, such as Han or Philip K. Dick Android, have been designed for experimental and cultural purposes.
While it seems a distant reality that robots will eventually become self-aware, the company raises an interesting debate: "What will it be like to live with machines that resemble us and almost behave like a human being?
Figure AI
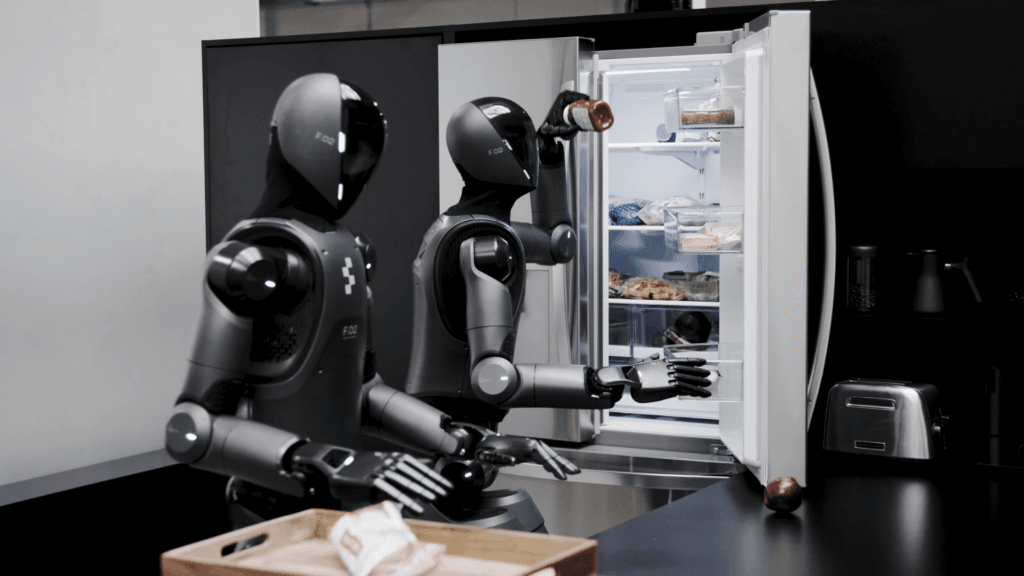
Figure AI is a startup founded in 2022 with the ambitious goal of developing a generalist humanoid robot capable of taking on physical tasks in a wide variety of sectors. Its first model, Figure 01, attracted industry-wide attention as it was able to combine advanced bipedal locomotion with state-of-the-art artificial intelligence, allowing it to interact with people and complex environments in a "smart" way.
In this sense, Figure 01 was already capable of understanding natural language and acting with contextual autonomy, for which it signed a strategic partnership agreement with OpenAI, allowing it to incorporate models similar to those used in systems such as ChatGPT.
In 2024, the company introduced Figure 02, which improves locomotion with batteries integrated into the torso, five articulated fingers per hand, RGB cameras and a powerful AI stack that allows it to hold real-time conversations. All this has resulted in agreements with companies such as BMW, where the robots are already "working" in one of its plants, or with UPS, where their efficiency is being tested for the development of logistics tasks.
The truth is that humanoid robotics, driven by artificial intelligence, is ceasing to be a futuristic promise to become a technology with real applications. The companies discussed in this article are not only designing machines capable of mimicking the human body, they are laying the groundwork for a new era of human-robot collaboration. As these technologies are perfected, we are likely to see humanoids move from being a rarity to becoming a regular part of our working environment. But are we ready?
Read more
Tesla and Optimus: the vision of Elon Musk
What is the difference between human-centred robotics and industrial robotics?